Publications
2024
- Sentimental Analysis on the Informativeness of Cybersecurity Disclosure: Are firms aware of their software vulnerabilities?Hongmin Du, Linda Du, Xiao Li, and 1 more authorPre-Print, 2024
- A Novel Framework for Textual Extraction on Cybersecurity DisclosureHongmin Du, Xiao Li, Miklos Vasarhelyi, and 1 more authorPre-Print, 2024
In this paper we analyze that the sentiment of sentences plays an important role in evaluating positive or negative level of the text contents when measuring cybersecurity disclosure. In addition, the commonly existing irrelevant context and redundant context expressing similar semantic meaning bring massive noise in the measurement. The noise is hard to be avoided through simple keywords-based analysis and makes the measurement considerably unreliable. To tackle the above two issues, we propose a novel textual extraction framework that derives cybersecurity disclosure sentiment scores for given 10-K files. In the textual extraction framework, an unsupervised topic extraction algorithm first proposed to group texts into different topics, then a cybersecurity filter based on similarity is applied to select all cybersecurity topics. Next three topic summarization algorithms are proposed to produce summaries of cybersecurity topics, namely Inter-Topic Summarization Algorithm, Intra-Topic Summarization Algorithm and Cybersecurity Constrained Intra-Topic Summarization Algorithm. With the remarkable effects of topic extraction and summarization algorithms, the noise information is significantly reduced. The \textbfScore \textbfof \textbfSentiment (SoS) is further designed to quantify the cybersecurity disclosure by evaluating the sentiment of sentences in the cybersecurity topics enclosed in summaries. We finally illustrate the score of sentiment and demonstrate the effectiveness of proposed framework on a sample of real 10-K dataset.
-
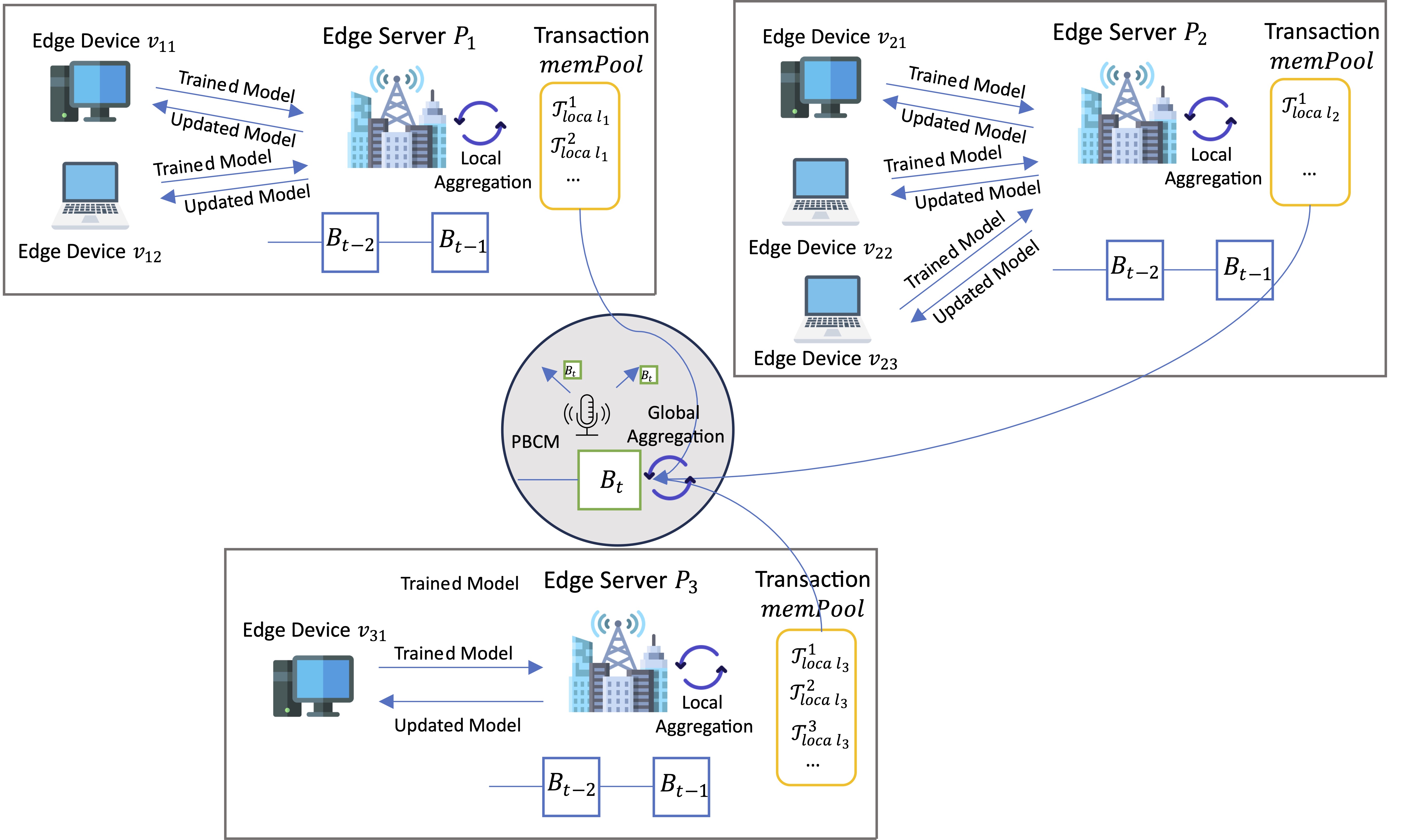 A Blockchain-empowered Multi-Aggregator Federated Learning Architecture in Edge Computing with Deep Reinforcement Learning OptimizationXiao Li, and Weili WuPre-Print, 2024
A Blockchain-empowered Multi-Aggregator Federated Learning Architecture in Edge Computing with Deep Reinforcement Learning OptimizationXiao Li, and Weili WuPre-Print, 2024Federated learning (FL) is emerging as a sought-after distributed machine learning architecture, offering the advantage of model training without direct exposure of raw data. With advancements in network infrastructure, FL has been seamlessly integrated into edge computing. However, the limited resources on edge devices introduce security vulnerabilities to FL in the context. While blockchain technology promises to bolster security, practical deployment on resource-constrained edge devices remains a challenge. Moreover, the exploration of FL with multiple aggregators in edge computing is still new in the literature. Addressing these gaps, we introduce the Blockchain-empowered Heterogeneous Multi-Aggregator Federated Learning Architecture (BMA-FL). We design a novel light-weight Byzantine consensus mechanism, namely PBCM, to enable secure and fast model aggregation and synchronization in BMA-FL. We also dive into the heterogeneity problem in BMA-FL that the aggregators are associated with varied number of connected trainers with Non-IID data distributions and diverse training speed. We propose a multi-agent deep reinforcement learning algorithm to help aggregators decide the best training strategies. The experiments on real-word datasets demonstrate the efficiency of BMA-FL to achieve better models faster than baselines, showing the efficacy of PBCM and proposed deep reinforcement learning algorithm.
-
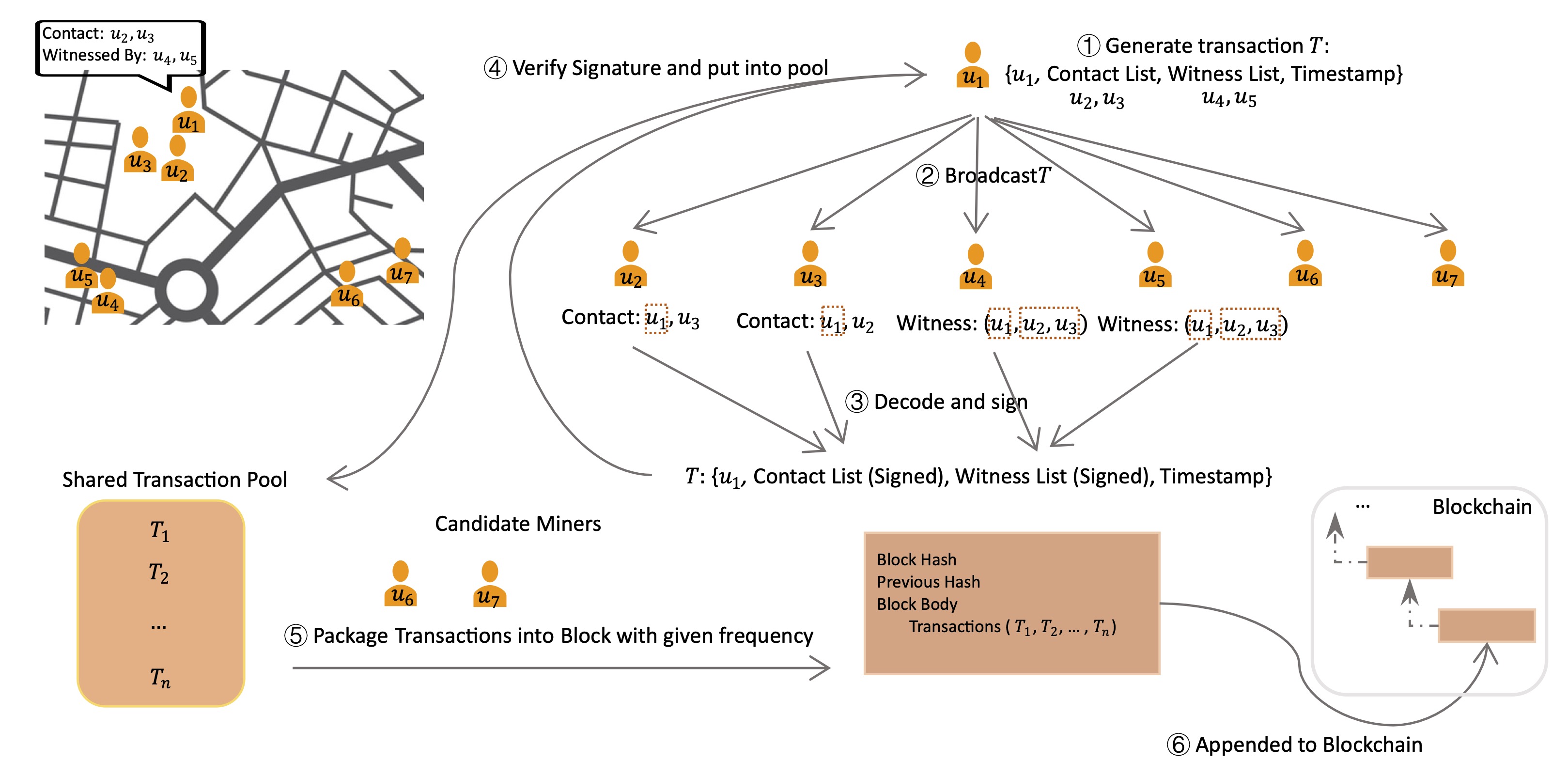 Blockchain-Driven Privacy-Preserving Contact-Tracing Framework in PandemicsXiao Li, Weili Wu, and Tiantian ChenIEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2024
Blockchain-Driven Privacy-Preserving Contact-Tracing Framework in PandemicsXiao Li, Weili Wu, and Tiantian ChenIEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2024Blockchain technology, recognized for its decentralized and privacy-preserving capabilities, holds potential for enhancing privacy in contact tracing applications. Existing blockchain-based contact tracing frameworks often overlook one or more critical design details, such as the blockchain data structure, a decentralized and lightweight consensus mechanism with integrated tracing data verification, and an incentive mechanism to encourage voluntary participation in bearing blockchain costs. Moreover, the absence of framework simulations raises questions about the efficacy of these existing models. To solve above issues, this article introduces a fully third-party independent blockchain-driven contact tracing (BDCT) framework, detailed in its design. The BDCT framework features an Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption-based transaction verification method (RSA-TVM), achieving over 96% accuracy in contact case recording, even with a 60% probability of individuals failing to verify contact information. Furthermore, we propose a lightweight reputation corrected delegated proof of stake (RC-DPoS) consensus mechanism, coupled with an incentive model, to ensure timely reporting of contact cases while maintaining blockchain decentralization. Additionally, a novel simulation environment for contact tracing is developed, accounting for three distinct contact scenarios with varied population density. Our results and discussions validate the effectiveness, robustness of the RSA-TVM and RC-DPoS, and the low storage demand of the BDCT framework.
2023
-
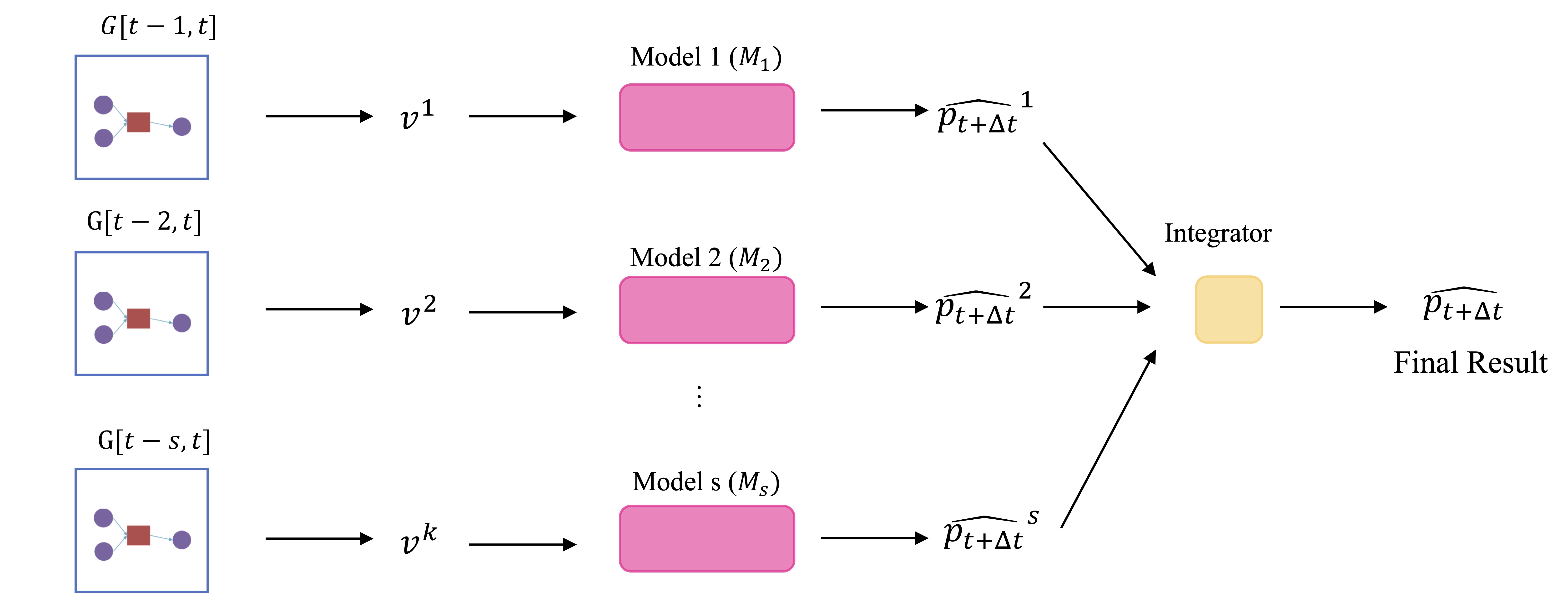 Bitcoin daily price prediction through understanding blockchain transaction pattern with machine learning methodsXiao Li, and Linda DuJ. Comb. Optim., 2023
Bitcoin daily price prediction through understanding blockchain transaction pattern with machine learning methodsXiao Li, and Linda DuJ. Comb. Optim., 2023Bitcoin has became one of the most popular investment asset recent years. The volatility of bitcoin price in financial market attracting both investors and researchers to study the price changing manners of bitcoin. Existing works try to understand the bitcoin price change by manually discovering features or factors that are assumed to be reasons of price change. However, the trivial feature engineering consumes human resources without the guarantee that the assumptions or intuitions are correct. In this paper, we propose to reveal the bitcoin price change through understanding the patterns of bitcoin blockchain transactions without feature engineering. We first propose k-order transaction subgraphs to capture the patterns. Then with the help of machine learning models, Multi-Window Prediction Framework is proposed to learn the relation between the patterns and the bitcoin prices. Extensive experimental results verify the effectiveness of transaction patterns to understand the bitcoin price change and the superiority of Multi-Window Prediction Framework to integrate multiple submodels trained separately on multiple history periods.
- Machine Learning with Low-Resource Data from Psychiatric ClinicsHongmin W. Du, Neil De Chen, Xiao Li, and 1 more authorIn Combinatorial Optimization and Applications - 17th International Conference, COCOA 2023, Hawaii, HI, USA, December 15-17, 2023, Proceedings, Part II, 2023
Amidst the rapid growth of big data, the success of machine learning is critically tethered to the availability and quality of training data. A pertinent challenge faced by this symbiotic relationship is the issue of “low-resource data,” characterized by insufficient data volume, diversity, and representativeness, and exacerbated by class imbalances within datasets. This study delves into the intersection of machine learning and big data, exploring innovative methodologies to counteract the challenges of data scarcity. Focusing on psychiatric clinic data, marked by subjectivity and inconsistency, we outline the unique challenges posed by the nature of data in this domain. To address these challenges, we explore the potential of data augmentation-using transformations or operations on available data-and transfer learning, where knowledge from a pre-trained model on a large dataset is transferred to a smaller one. Through a comprehensive exploration of these methodologies, this research aims to bolster the effectiveness of machine learning in low-resource environments, with a vision of advancing the digital landscape while navigating inherent data constraints.
2022
-
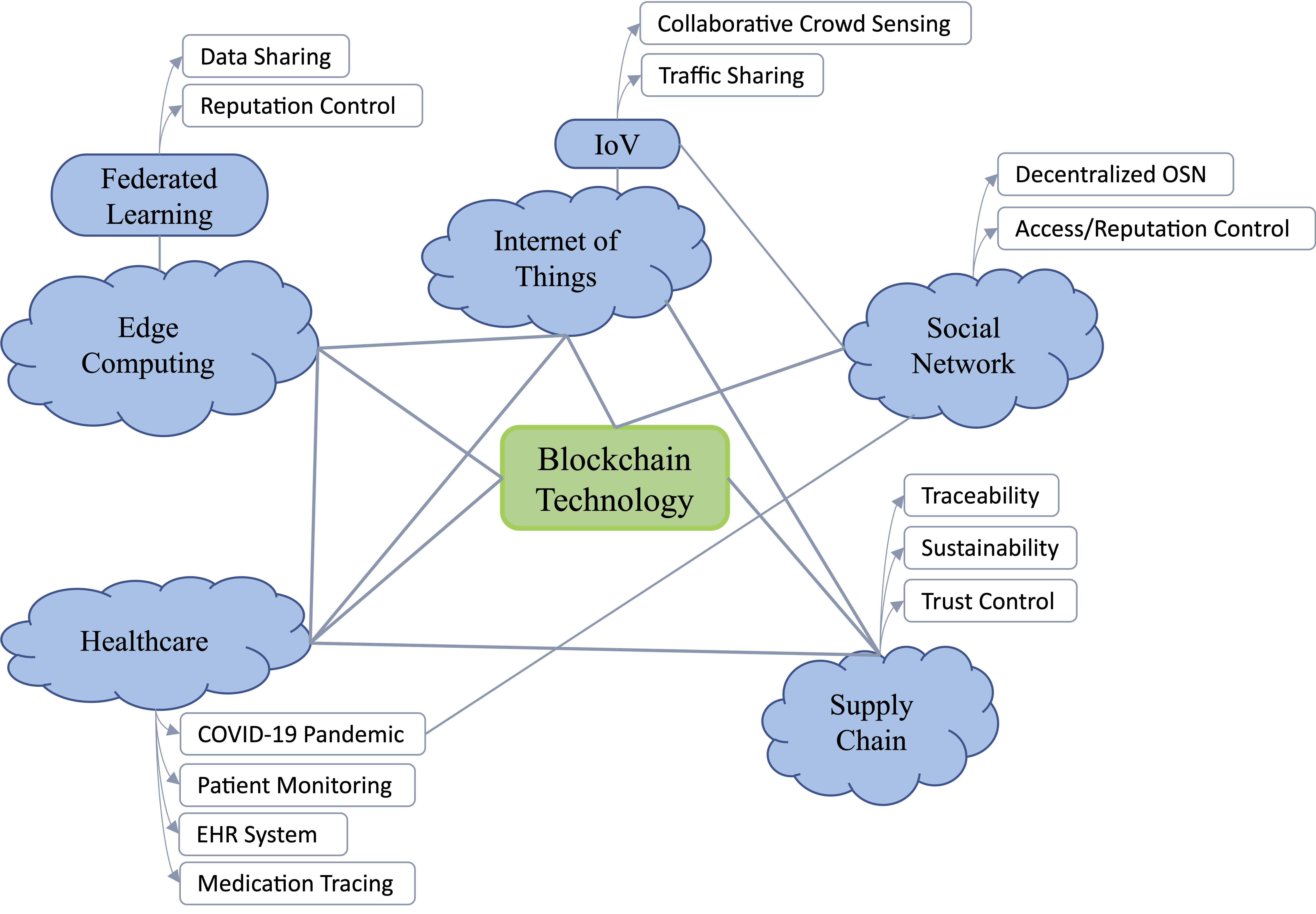 Recent Advances of Blockchain and Its ApplicationsXiao Li, and Weili WuJournal of Social Computing, Dec 2022
Recent Advances of Blockchain and Its ApplicationsXiao Li, and Weili WuJournal of Social Computing, Dec 2022Blockchain is an emerging decentralized data collection, sharing, and storage technology, which have provided abundant transparent, secure, tamper-proof, secure, and robust ledger services for various real-world use cases. Recent years have witnessed notable developments of blockchain technology itself as well as blockchain-enabled applications. Most existing surveys limit the scopes on several particular issues of blockchain or applications, which are hard to depict the general picture of current giant blockchain ecosystem. In this paper, we investigate recent advances of both blockchain technology and its most active research topics in real-world applications. We first review the recent developments of consensus and storage mechanisms and communication schema in general blockchain systems. Then extensive literature review is conducted on blockchain-enabled Internet of Things (IoT), edge computing, federated learning, and several emerging applications including healthcare, COVID-19 pandemic, online social network, and supply chain, where detailed specific research topics are discussed in each. Finally, we discuss the future directions, challenges, and opportunities in both academia and industry.
- Energy efficiency optimization for multiple chargers in Wireless Rechargeable Sensor NetworksYi Hong, Chuanwen Luo, Deying Li, and 3 more authorsTheor. Comput. Sci., Dec 2022
To guarantee the continuous coverage of the rechargeable sensors, Wireless Rechargeable Sensor Networks (WRSNs) has emerged with the advantages of high charging efficiency and reliable charging timeliness. Charging planning is an important problem in theoretical research and practical applications, and it faces more difficulties and challenges for multiple mobile chargers. In this paper, we introduce a charging planning problem for multiple chargers, namely Charging Energy Efficiency Maximization problem for Multi-Chargers in WRSNs (CEEM-MC Problem), and prove its NP-hardness. The problem aims to maximize the charging energy efficiency of the charging process by assigning the charging amount and planning the charging path. To balance the charging consumption among multiple chargers, we propose two algorithms which are different on the charging path planning, Ring-Wandering Algorithm and Eight-Wandering Algorithm. To evaluate the performance on energy efficiency, we perform a series of simulations and the results verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms.
2021
- A Multi-window Bitcoin Price Prediction Framework on Blockchain Transaction GraphXiao Li, and Linda DuIn Algorithmic Aspects in Information and Management - 15th International Conference, AAIM 2021, Virtual Event, December 20-22, 2021, Proceedings, Dec 2021
Bitcoin, as one of the most popular cryptocurrency, has been attracting increasing attention from investors. Consequently, bitcoin price prediction is a rising academic topic. Existing bitcoin prediction works are mostly based on trivial feature engineering, that is, manually designed features or factors from multiple areas. Feature engineering not only requires tremendous human effort, but the effectiveness of the intuitively designed features can not be guaranteed. In this paper, we aim to mine the abundant patterns encoded in Bitcoin transactions, and propose k-order transaction graphs to reveal patterns under different scopes. We propose features based on a transaction graph to automatically encode the patterns. The Multi-Window Prediction Framework is proposed to train the model and make price predictions, which can take advantage of patterns from different historical periods. We further demonstrate that our proposed prediction method outperforms the state-of-art methods in the literature.
- Maximizing Energy Efficiency for Charger Scheduling of WRSNsYi Hong, Chuanwen Luo, Zhibo Chen, and 2 more authorsIn Algorithmic Aspects in Information and Management - 15th International Conference, AAIM 2021, Virtual Event, December 20-22, 2021, Proceedings, Dec 2021
Wireless Rechargeable Sensor Networks (WRSNs) has emerged with the advantages of high charging efficiency, which can guarantee the timeliness of charging and the service quality of network coverage. To guarantee the continuous coverage of the rechargeable sensors, continuous power supply for sensors becomes more important. In this paper, we focus on the Charging Scheduling problem with Maximized Energy Efficiency in WRSNs (CS-MEE Problem), in which a mobile charger is used to charge the low energy sensors in WRSN. The problem aims to optimize travelling path of the mobile charger for maximizing the charging energy efficiency of the charging process. We firstly give the mathematical model and NP-hardness proof of the problem. Then we propose an heterogeneous-weighted-graph algorithm, called CS-HWG, to solve the problem. To evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm, the extensive simulation experiments are conducted under four influencing factors in terms of the energy efficiency of the mobile charger to verify the effectiveness of the algorithm.
2019
-
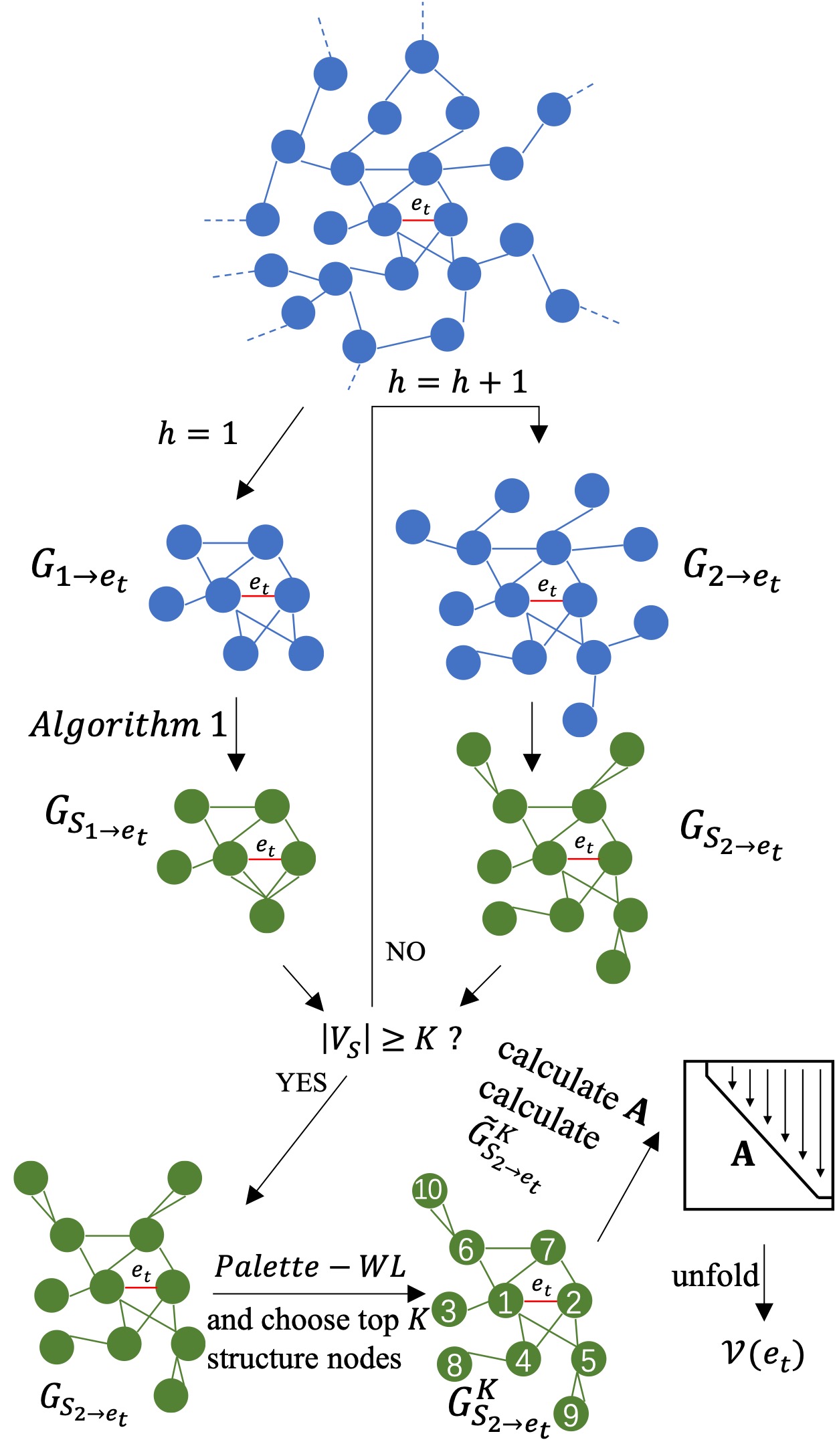 A Universal Method Based on Structure Subgraph Feature for Link Prediction over Dynamic NetworksXiao Li, Wenxin Liang, Xianchao Zhang, and 2 more authorsIn 2019 IEEE 39th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Jul 2019
A Universal Method Based on Structure Subgraph Feature for Link Prediction over Dynamic NetworksXiao Li, Wenxin Liang, Xianchao Zhang, and 2 more authorsIn 2019 IEEE 39th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Jul 2019In dynamic networks, links are annotated with timestamps showing the emerging time and the link prediction problem is to infer the future links in networks. Universal link prediction methods are highly demanded in various applications, which require universal link features that are feasible for multiple kinds of network topological structures and capable to address the difference of links with different timestamps. In this paper, we propose a novel link feature called Structure Subgraph Feature (SSF). The SSF is an outstanding link feature that is feasible to various dynamic networks due to the following superiorities: (1) the proposed structure subgraph is so far the most effective manner to represent surrounding topological features of target link and (2) the normalized influence well specifies the influence of multiple links and different timestamps in structure subgraph. We finally propose two link prediction methods by applying SSF to a linear regression model and a neural machine. Experimental results on real-world dynamic network datasets indicate that the SSF-based methods consistently provide top-class performance on various dynamic networks.
- Influence Maximization in Signed Social Networks With Opinion FormationWenxin Liang, Chengguang Shen, Xiao Li, and 3 more authorsIEEE Access, 2019
Influence maximization (IM) has been widely studied in recent years. Given fixed number of seed users and certain diffusion models, the IM problem aims to select proper seed users in a social networks such that they can achieve the maximal spread of influence. Most previous work assumes that there are only positive relationships between users, and thus users spread influence positively. However, negative relationships also universally exist in various social networks and are complementary to positive relationships in information diffusion. In this paper, the influence maximization problem is addressed in signed social networks that contain both positive and negative relationships. We propose a novel diffusion model called LT-S and two influence spread functions. The proposed LT-S model extends the classical linear threshold model with opinion formation that incorporates both positive and negative opinions and simulates information diffusion in real-world social networks. The influence spread functions under the LT-S model are neither monotone nor submodular which bring challenges to maximization. The RLP algorithm is proposed to tackle the issue, which is improved from R-Greedy algorithm by incorporating two proposed accelerating techniques, the live-edge based and propagation-path based techniques. The results of the extensive experiments on public real signed social network datasets demonstrate that our algorithm outperforms the baseline algorithms in terms of both efficiency and effectiveness.
2018
- Supervised ranking framework for relationship prediction in heterogeneous information networksWenxin Liang, Xiao Li, Xiaosong He, and 2 more authorsAppl. Intell., 2018
In recent years, relationship prediction in heterogeneous information networks (HINs) has become an active topic. The most essential part of this task is how to effectively represent and utilize the important three kinds of information hidden in connections of the network, namely local structure information (Local-info), global structure information (Global-info) and attribute information (Attr-info). Although all the information indicates different features of the network and influence relationship creation in a complementary way, existing approaches utilize them separately or in a partially combined way. In this article, a novel framework named Supervised Ranking framework (S-Rank) is proposed to tackle this issue. To avoid the class imbalance problem, in S-Rank framework we treat the relationship prediction problem as a ranking task and divide it into three phases. Firstly, a Supervised PageRank strategy (SPR) is proposed to rank the candidate nodes according to Global-info and Attr-info. Secondly, a Meta Path-based Ranking method (MPR) utilizing Local-info is proposed to rank the candidate nodes based on their meta path-based features. Finally, the two ranking scores are linearly integrated into the final ranking result which combines all the Attr-info, Global-info and Local-info together. Experiments on DBLP data demonstrate that the proposed S-Rank framework can effectively take advantage of all the three kinds of information for relationship prediction over HINs and outperforms other well-known baseline approaches.